World Bank
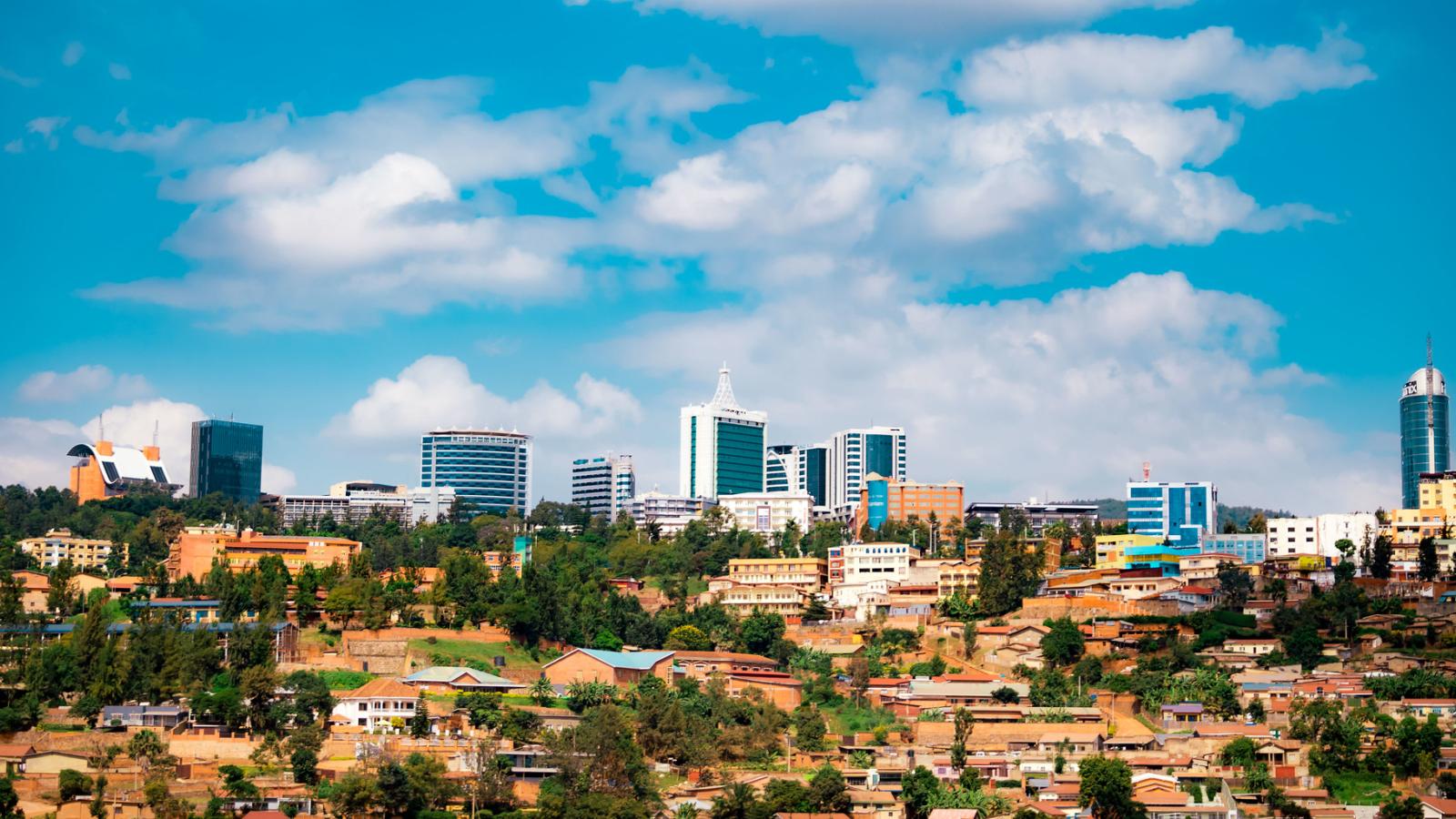
Rwanda
Rwanda is located in the Great Lakes region of East Africa and has an urban population of about 2.2 million. UrbanShift is engaged in the capital, Kigali, as well as six additional cities: Huye, Muhanga, Musanze, Nyagatare, Rubavu and Rusizi.
UrbanShift's intervention in Rwanda, known as the Rwanda Urban Development Project (RUDP II), is based on the country's National Urbanization Policy. RUDP II is implemented by the World Bank in partnership with the Government of Rwanda, City of Kigali, and participating city administrations.
The East African nation of Rwanda encompasses diverse habitats and ecosystems, including humid montane forests, savannahs, lakes, rivers and wetlands. These ecosystems support a wide range of biodiversity and provide essential ecosystem services that underpin lives and livelihoods.
Rwanda is also one of the fastest-growing economies in the region and has made significant progress over the last two decades in alleviating poverty and improving literacy rates, access to healthcare, and gender equity. In 2008, Rwanda became the first nation in the world to elect a majority of women parliamentarians.
In line with its Vision 2050 pathway, Rwanda seeks to make significant long-term investments in people and the economy, with the objective of becoming an upper-middle-income country by 2035 and a high-income country by 2050.
- POPULATION
-
12.6 million
- ECONOMIC DRIVERS
-
Agriculture, Industry & Tourism
- URBANIZATION
-
17.4%
THE CHALLENGE
While Rwanda has been investing a large share of its public funds in infrastructure development and services, there remains a large infrastructure gap in the country. This gap occurs predominantly in the housing sector, as Rwanda faces rapid urbanization owing to rural-urban migration. Population growth coupled with urban expansion threatens the country's ecosystems and biodiversity and increases vulnerability to flood risks, land degradation and climate-related events.
The Rwandan government has taken concrete steps to address some of these challenges through policy as well as on-the-ground implementation of supporting programs. For e.g., Rwanda achieved its target of increasing forest cover from 24.5% to more than 30% between 2012 and 2020, leading to enhanced carbon storage and sequestration potential.
Nevertheless, Rwanda remains highly vulnerable to climate change. Exposure to climate-related risks can undermine vital gains in poverty reduction and impede economic growth, as well as accelerate the loss of biodiversity. Rwanda also faced its first recession in 2020, as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. A subsequent rise in poverty was noted in the rural areas, which is likely to drive more migration to Kigali and other urban centers.
URBANSHIFT'S INTERVENTION
The Rwanda Urban Development Project (RUDP II) aims to improve access to basic services, enhance resilience to climate risks and natural disasters and strengthen integrated urban planning and management in the City of Kigali and six additional cities, namely Huye, Muhanga, Musanze, Nyagatare, Rubavu and Rusizi. This will be achieved through a combination of physical (grey) and nature-based (green) solutions, demonstrating how the two approaches complement each other and the ways in which they can be replicated. RUDP II will be implemented on the ground from January 2021 - June 2025.
Examples of RUDP II activities:
- Wetland rehabilitation
- Green and grey investments to mitigate erosion, reduce and manage stormwater runoff along settlements, enhance wetland buffer zones and address flood hotspots
- Comprehensive technical support to improve citywide flood risk management, such as development of a stormwater master plan and solid waste strategy.

KIGALI
Located in the lush, hilly heart of Rwanda, the capital city, Kigali, is home to 1.63 million people, or approximately 14% of the country's total population. As Rwanda's financial and administrative hub, Kigali accounts for over 40% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and attracts large numbers of rural migrants, resulting in a range of urban challenges: limited infrastructure to serve a growing population, limited green spaces, a decline in natural drainage systems, and a shortfall of safe, affordable housing. Today, 63% of Kigali's residential settlements are considered informal or unplanned.
One of RUDP II's interventions in Kigali consists of the rehabilitation of critical wetlands to improve the ecosystem services on which many of the city's residents depend.
HUYE
The city of Huye is the main urban center of southern Rwanda and is located along the national highway that connects Kigali to neighboring DRC (Democratic Republic of the Congo). Huye has a population of about 41,000, with a built-up area that has expanded from 1 km2 to 9 km2 in the last three decades.
The Rwandan government is committed to accelerating socio-economic growth in Huye by developing basic infrastructure, expanding the industrial park, and establishing the city as a research and educational hub.
MUHANGA
Muhanga is located southwest of Kigali and has a population of 44,000 inhabitants. Most of the city's natural vegetation has been lost to agricultural activities, which constitute the primary source of livelihood for the residents of Muhanga and surrounding areas. The local economy is also fuelled by trade, industry, construction and mining. Given the presence of a large number of businesses in Muhanga and its proximity to Kigali, the city is poised to become an important commercial and financial hub.
To accelerate local economic growth and enhance living conditions in Muhanga, the government plans to invest in basic infrastructure, improve waste management facilities, develop an eco-business park to boost agricultural processing capacity, and expand the road network to include green modes of transportation.
MUSANZE
Located in the Northern Province, the city of Musanze is home to over 102,000 people. Out of the six secondary cities that UrbanShift is engaged with in Rwanda, Musanze has the highest population density and lowest poverty rate. The local economy is driven by tourism, construction, agriculture and the arts, while the presence of financial institutions has supported the growth of key industries and enabled infrastructure development within the city.
To further expand its economy, Musanze city is working with the national government to improve basic infrastructure and services and continue to strengthen the tourism and agribusiness sector.
NYAGATARE
The city of Nyagatare is located in the Eastern Province and has a population of roughly 47,000. Unlike most of Rwanda, which is hilly, Nyagatare has relatively flat topography. The local economy is dominated by agriculture, and with vast expanses of unoccupied land, cattle breeding has become an important activity.
The city's rapid growth has put extreme pressure on the delivery of basic infrastructure and services, which are lagging behind. The administration of Nyagatare is determined to compensate for this shortcoming by improving access to essential urban services in order to support the city's current and projected population.
RUBAVU
Located in the Western Province, Rubavu is home to approximately 150,000 inhabitants and is the fastest urbanizing city in Rwanda. Tourism is a key pillar of this dynamic city, as a result of its proximity to Lake Kivu, Virunga National Park and Gishwati Forest. Rubavu has a well-developed tourism infrastructure and also plays a strategic role in trade with neighboring DRC.
To accelerate Rubavu's economic growth, the local administration and national government counterparts are prioritizing expanding the coverage of basic infrastructure, further developing the tourism sector, and establishing the city as a center of logistics and transport, as well as a cultural hub.
RUSIZI
Rusizi is situated in the Western Province, bordering DRC and Burundi, and has a population of 63,000. The city is an important trading center, facilitated by the presence of the Kamembe International Airport. Access to maritime transport has also improved regional trade, allowing Rusizi to establish itself as one of the largest commercial hubs in the country. However, agriculture remains the largest source of employment in the area.
To boost Rusizi's economy, the city administration and national government are planning to further develop the port facilities, maritime transport infrastructure and road networks, as well as improve access to basic urban services.
PROJECT BUDGET
- GEF Grant: $8 million
- Co-financing: $150 million
Regional Coordinator
Jessy Appavoo coordinates UrbanShift's capacity-building activities in Rwanda.
Related Content
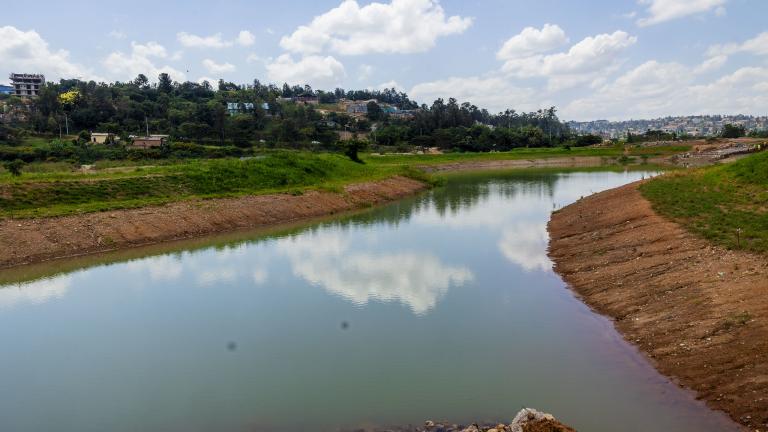

Breathing New Life into 5 Kigali Wetlands to Enhance Climate Resilience and Quality of Life
These formerly degraded sites will soon welcome visitors for recreational and educational opportunities—while alleviating flood challenges for the city.

Rwanda Second Multilevel Governance Dialogue - Local Government Consultation on NDC 3.0 Development
This dialogue will strengthen local government involvement in shaping and implementing the country’s NDC 3.0, fostering national-local collaboration for ambitious climate action.

Flood Resilience and Biodiversity in Focus: Rwanda’s Vision for Sustainable and Resilient Cities
The first Dialogue in Rwanda brought together national and local governments, development partners, and experts to develop strategies for flood resilience and biodiversity in Rwandan cities, aligning local priorities with national urban policies.

Kigali, Rwanda: Imbuga City Walk Car-Free Zone
Model: Public-Private Partnerships


